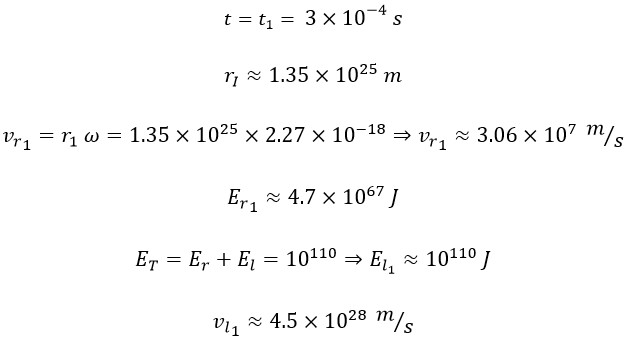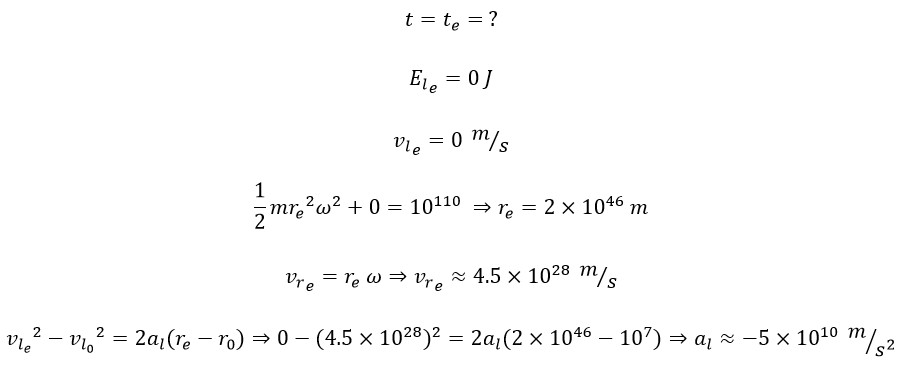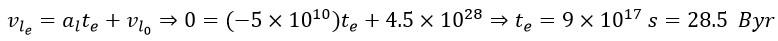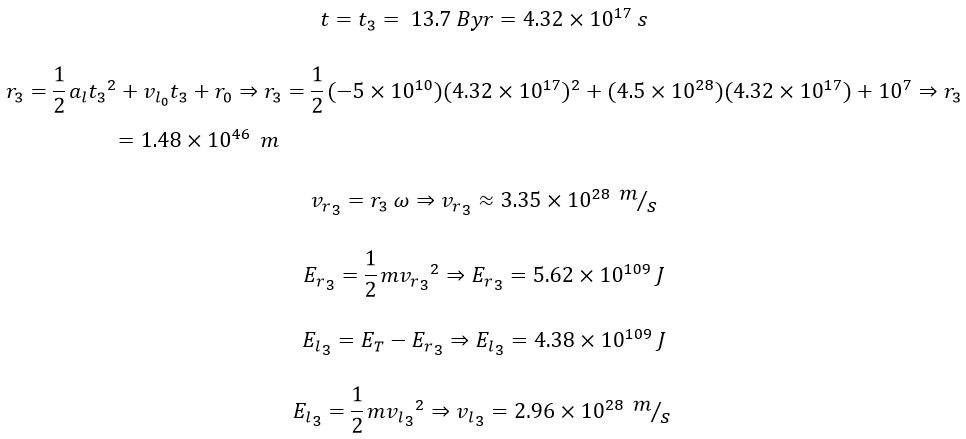
New Computational Table of Physical Parameters for the Moments of Beginning, Inflation, Present, and End of the Universe 2025
If we observe the Moon, we notice that it revolves around the Earth. The Earth itself is orbiting the Sun, and the Sun revolves around the central black hole of the Milky Way galaxy. As mentioned in previous articles [1], the primary motion in the universe is rotational. Furthermore, we have demonstrated that Hubble's law provides evidence for the existence of rotational motion in the universe. The speed described in Hubble's law is tangential speed, which depends on two factors: the distance from the centre, "D=r" and the Hubble constant, "H=ω" which represents the constant angular speed [2].
However, our universe also originates from a massive explosion, the Big Bang. This explosion generates linear motion. Therefore, to determine the physical parameters of the universe at different times, it is essential to consider both the rotational motion with constant angular velocity and the linear motion simultaneously. On the other hand, in previous articles [3], using the Monte Carlo method, we have calculated the total energy of the universe (ET) at the moment of the Big Bang, which was approximately 10110 joules. In this article, by applying the principle of energy conservation, we calculate various parameters from the initial moments of the Big Bang, through the end of the cosmic inflationary stage, to the present time, the time of equality between linear and rotational energy, and finally, the end of the universe. The results are presented in a table at the end of this article.
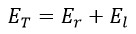
Here, Er represents rotational energy, and El represents linear energy. By utilising the definitions of linear and rotational energy, these two parameters are expressed in terms of the total mass of the universe, m = 1053 kg; the radius of rotation, r; the angular velocity (which is constant and equivalent to the Hubble constant ω = H = 2.27 × 10-18 s-1); and the linear speed "vl":
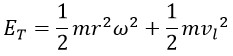
In previous articles [3], we have demonstrated that the universe was a spherical at the time of the Big Bang, with a size somewhere between the Earth and the Moon r0 ≈ 107 m. Given the radius of the universe at the moment of the Big Bang, the contribution of rotational energy was negligible and could be ignored. Therefore, at the time of the Big Bang, the total energy can be considered to arise entirely from linear motion:
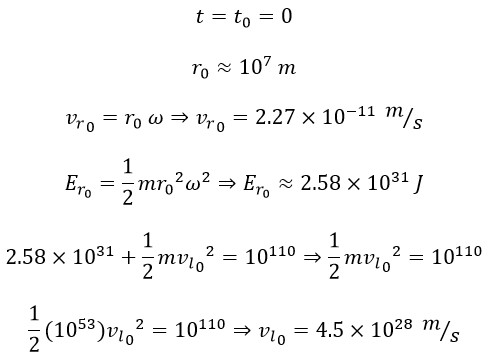
In previous article [4], using the density of the universe, we have calculated the radius of the universe (r1) at the end of the inflationary phase. Thus, we have:
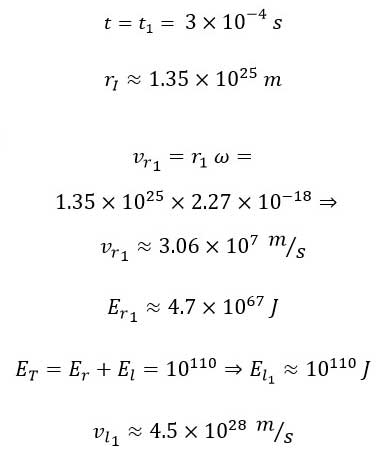
As indicated—and as discussed in previous articles—over time, the amount of linear energy decreases, and an equivalent amount is added to the rotational energy [5]. This implies that at the end of the universe’s outward trajectory, when it reaches its maximum radius, all the energy will be converted into rotational energy, and the linear energy will reduce to zero:
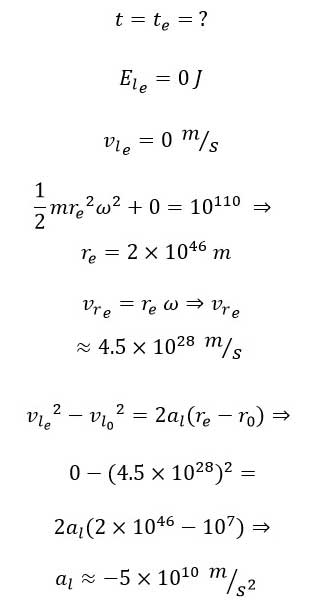
This represents the average deceleration that reduces the linear velocity (and consequently the linear energy). Thus, in linear motion, we observe a motion with constant negative acceleration.
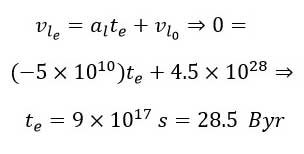
Next, we examine the time when the rotational and linear energies are equal:
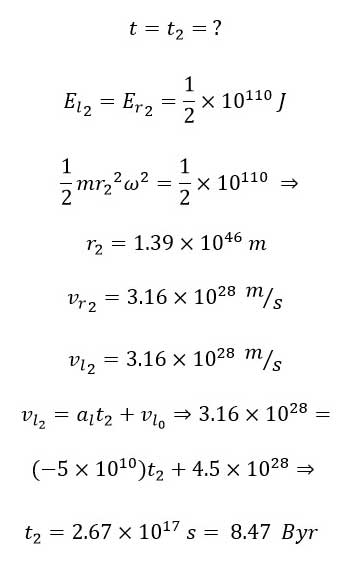
We now proceed to analyze the physical parameters of the universe at present.
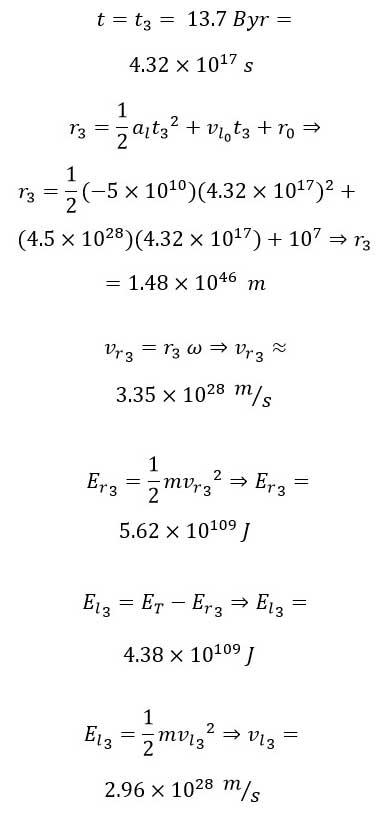
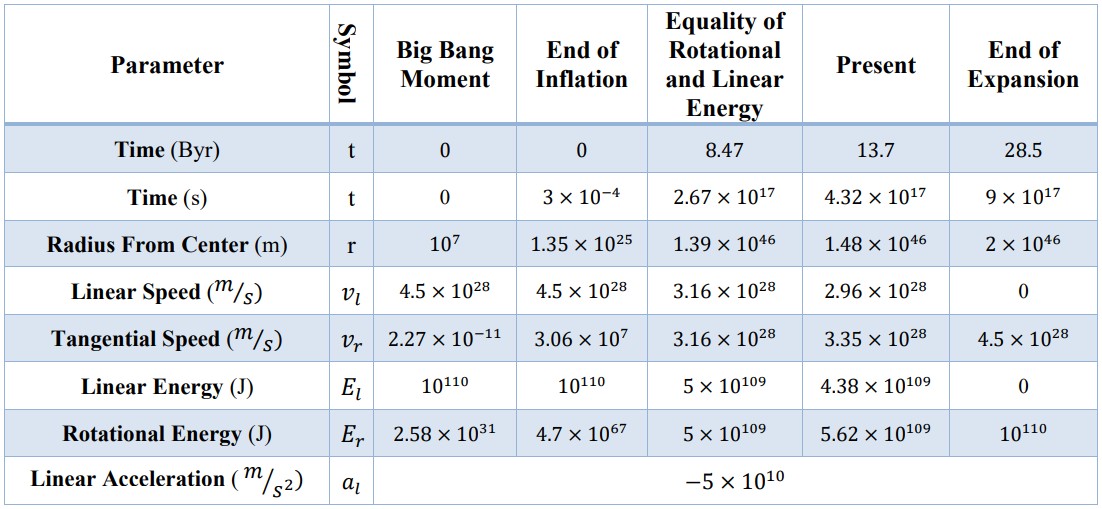
We present a summary of the results in the table below:
References:
[4] Saleh, Gh. " New Discoveries Using the Density of Galaxies in Universe 2025 (Elya Phenomenon)." Saleh Theory, 20 Jan. 2025, https://www.saleh-theory.com/article/new-discoveries-using-the-density-of-galaxies-in-universe-2025-elya-phenomenon
 Download PDF
Download PDF